[最新] global greenhouse gas emissions over time 212205
Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over timeGlobal Warming Potentials (GWPs) indicate the relative effectiveness of GHGs in trapping the Earth's heat over a certain time horizon The Global Warming Potential (GWP) was developed to allow comparisons of the global warming impacts of different gases Specifically, it is a measure of how much energy the emissions of 1 ton of a gas will absorb over a given period of time, relative to the emissions of 1 ton of carbon dioxide (CO 2)

Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions A By Type Of Gases B By Type Of Download Scientific Diagram
Global greenhouse gas emissions over time
Global greenhouse gas emissions over time-Greenhouse gas emissions could increase from 55 gigatons of CO2 equivalents (GtCO2e) in 19 to over 80 GtCO2e in 50 an almost 50 percent increase Causes of CO2emissions CO2emissions are mostly a result of burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas Over the past 171 years, human activities have raised atmospheric concentrations of CO 2 by 48% above preindustrial levels starting in 1850 This is more than what had happened naturally over a ,000 year period (from the Last Glacial Maximum to 1850, from 185 ppm to




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
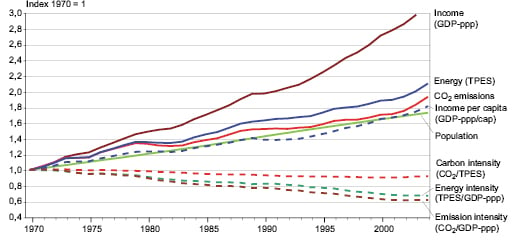
This chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnesWe classified Global greenhouse gas emissions as a national indicator Key findings Increasing trend Gross emissions of global GHGs increased 51 percent from 1990 to 13 This trend was assessed at the 95 percent confidence level Global gross and net emissions of GHGs continue to increase, driven largely by the energy sectorEmissions of carbon dioxide, the most important greenhouse gas, rose by about 80 percent during that time The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today far exceeds the natural range seen over the last 650,000 years
The graphs show monthly mean carbon dioxide measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii The carbon dioxide data on Mauna Loa constitute the longest record of direct measurements of CO 2 in the atmosphere They were started by C David Keeling of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in March of 1958 at a facility of the National Oceanic andThe Global Warming Potential (GWP) was developed to allow comparisons of the global warming impacts of different gases Specifically, it is a measure of how much energy the emissions of 1 ton of a gas will absorb over a given period of time, relative to the emissions of 1Human emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases – are a primary driver of climate change – and present one of the world's most pressing challenges 1 This link between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations – especially CO 2 – has been true throughout Earth's history 2 To set the scene, let's look at how the planet has warmed
Global lockdowns due to the pandemic reduced air pollution and lowered CO2 emissions, but due to the cumulative nature of greenhouse gases, the environmental relief is temporary, and the longterm problem remains Governments and businesses are addressing the greenhouse gas issue with policies to achieve more sustainable operations, and to Global Emissions Carbon dioxide emissions, primarily from the combustion of fossil fuels, have risen dramatically since the start of the industrial revolution Most of the world's greenhouse gas emissions come from a relatively small number of countriesGreenhouse Gas Emissions Need to Fall Over 7% Each Year We Must Stop Procrastinating Members of Christian youth groups from the Americas hold a
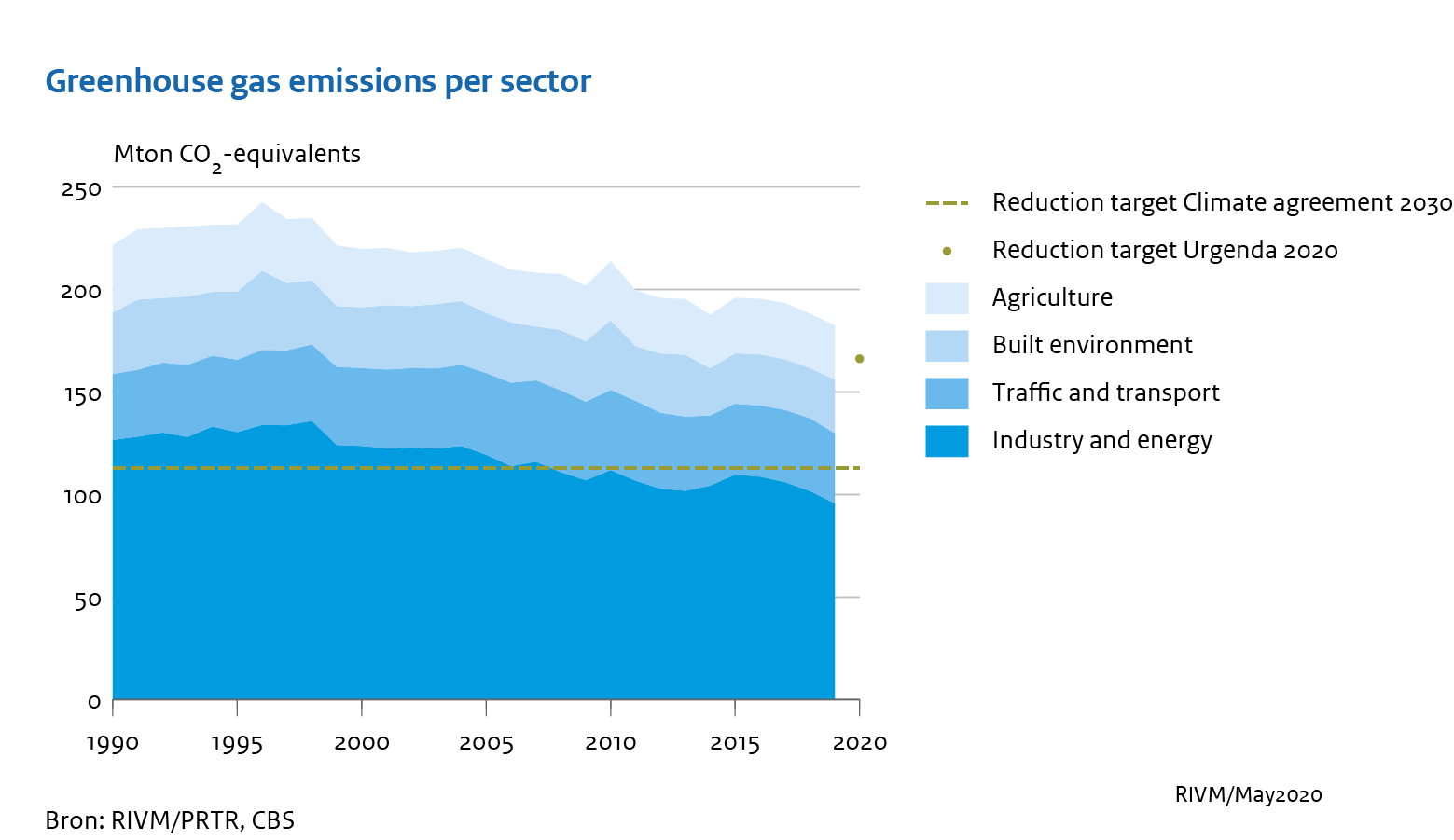



Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases Slightly Lower Again In 19 Rivm



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
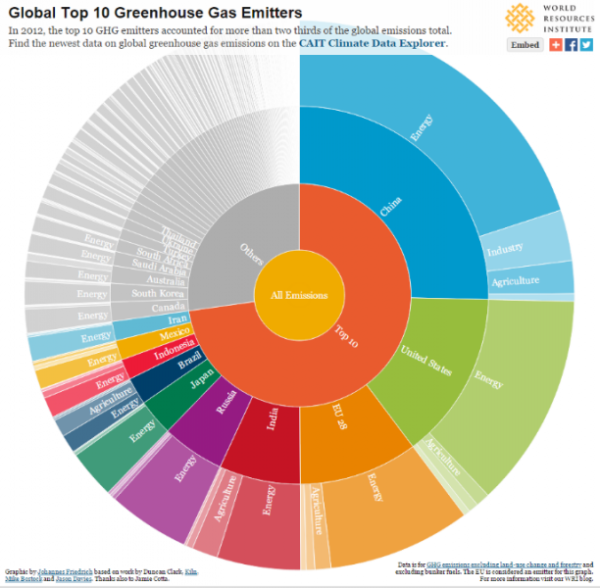
The Global Monitoring Division of NOAA's Earth System Research Laboratory has measured methane since 19 at a globally distributed network of air sampling sites ( Dlugokencky et al, 1994 ) A global average is constructed by first smoothing the data for each site as a function of time, and then smoothed values for each site are plotted as a And over time, the granularity of TRACE data will improve to provide the global community with the ability to view emissions from specific power plants, airports, forests, and countless otherIn 18, the highest emitting country was China with 12 355 Mt CO 2 eq, or 260% of global GHG emissions Since 05, emissions from China increased by 717% Canada's emissions Footnote 1 in 18 reached 725 Mt CO 2 eq, which made up 15% of global GHG emissions Greenhouse gas emissions for the world and the top 10 emitting countries and




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Ipcc We Can Still Stop Global Warming But It S Going To Be Tough Vox
In that report, methane has a global warming potential of 25, which means a ton of methane emissions contributes 25 times as much warming as a ton of carbon dioxide emissions over 100 years, and that ton of methane emissions is Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) Nitrous oxide occupies a relatively small share of global greenhouse gas emissions—about six percent—but it is 264 times more powerful than carbon dioxide over years Rising greenhouse gas emissions are the biggest cause of global warming and climate change The German and Swiss funded Energy Efficiency Building Refurbishment in Mongolia project mainly focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions from energy consumption in public and private buildings




Global Historical Co2 Emissions 1750 Statista




Net Phase Out Of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Newclimate Institute
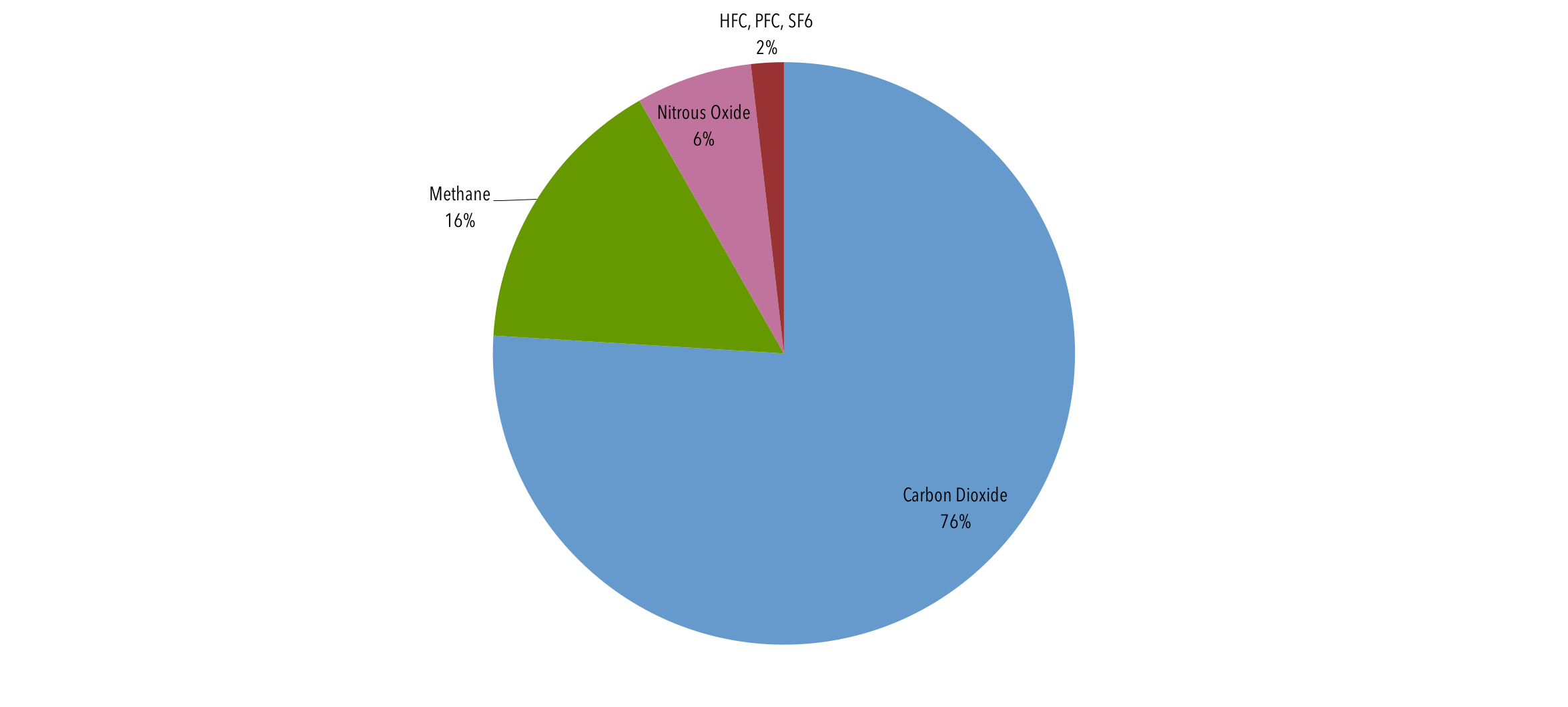
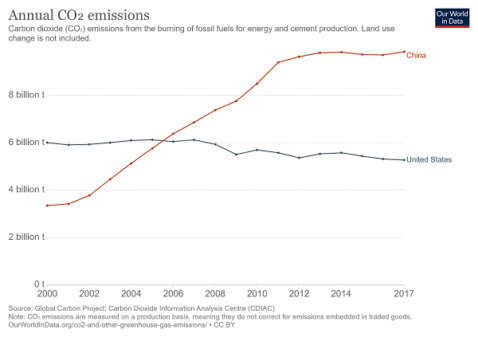
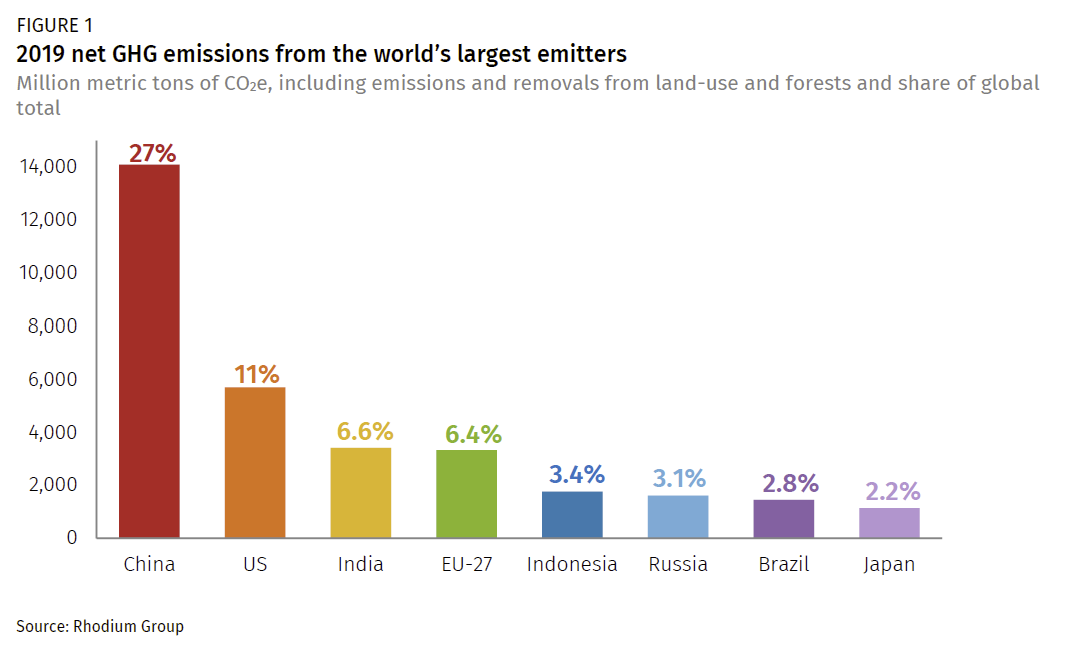
The world's countries emit vastly different amounts of heattrapping gases into the atmosphere The chart above and table below both show data compiled by the International Energy Agency, which estimates carbon dioxide (CO 2) emissions from the combustion of coal, natural gas, oil, and other fuels, including industrial waste and nonrenewable municipal wasteThe United States produced 66 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas emissions in 19, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person In 19 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GhG, followed by the United States with 11%, then IndiaA ccording to global EPA data the primary global greenhouse gas emissions are approximately 7680% carbon dioxide, 1016% methane, 57% nitrous oxide, and 23% fluorinated gases Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities, however, they have a high global




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Per Sector In 04 Total 50 Gtco 2 E Download Scientific Diagram



1
Russia (see Greenhouse gas emissions by Russia) 1,992 1630 2670 1381 Indonesia 1,704 506 Brazil 1,421 1050 524 Japan 1,155 1231 1310 1411 Iran 8 876 572 Germany 777 1 918 7 Canada (see Greenhouse gas emissions by Canada) 763 716 575 Mexico 695 718 528 Democratic Republic of the Congo 6 South Korea 673 732 634 Saudi Arabia 6384 rows Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Worldwide, net emissions of greenhouse gases fromThe planet's average surface temperature has risen about 212 degrees Fahrenheit (118 degrees Celsius) since the late 19th century, a change driven largely by increased carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere and other human activities 4 Most of the warming occurred in the past 40 years, with the seven most recent years being the warmest The years 16 and are tied for




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Over Time Forecast For 10 And Target Download Scientific Diagram




A Global Comparison Of The Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions Of Combustion Engine And Electric Passenger Cars International Council On Clean Transportation
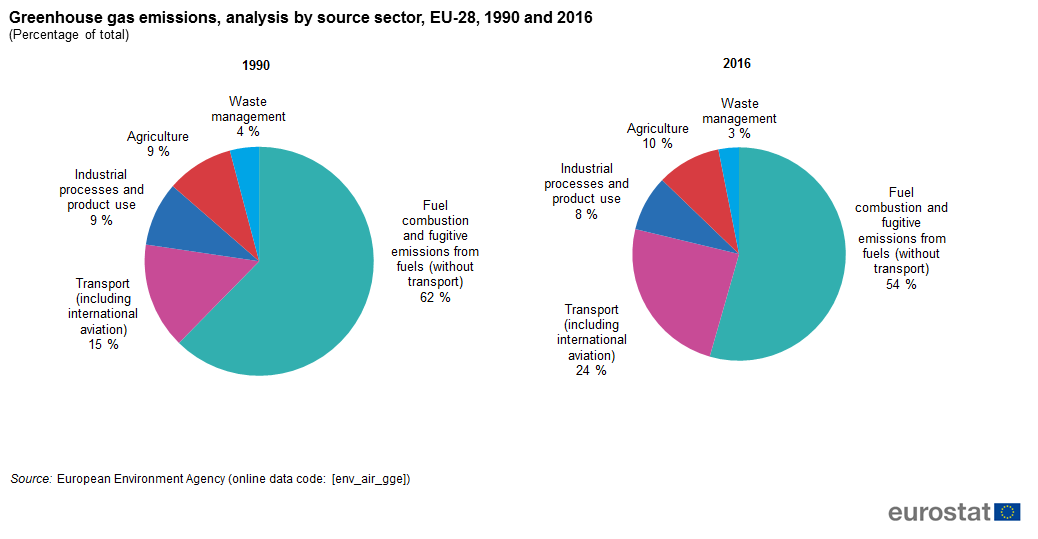
To find out more about the role of fluorinated gases in warming the atmosphere and their sources, visit the Fluorinated Greenhouse Gas Emissions page Emissions and Trends Overall, fluorinated gas emissions in the United States have increased by about 86 percent between 1990 and 19According to the Climate Data Explorer published by World Resources Institute, China, the European Union and the US contributed to more than 50% of global greenhouse gas emissions In 16, China's greenhouse gas emissions accounted for 26% of total global emissions The energy industry has been the biggest contributor to greenhouse gas emissions since the last decadeIn 18 emissions from fluorinated gases were 98 percent higher than 17 and 1515 percent higher than 05 Our net greenhouse gas emissions were 555 million tonnes, 572 percent higher than 1990 due to the underlying increase in gross emissions and a decrease in carbon uptake by New Zealand's plantation forest




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions A By Type Of Gases B By Type Of Download Scientific Diagram
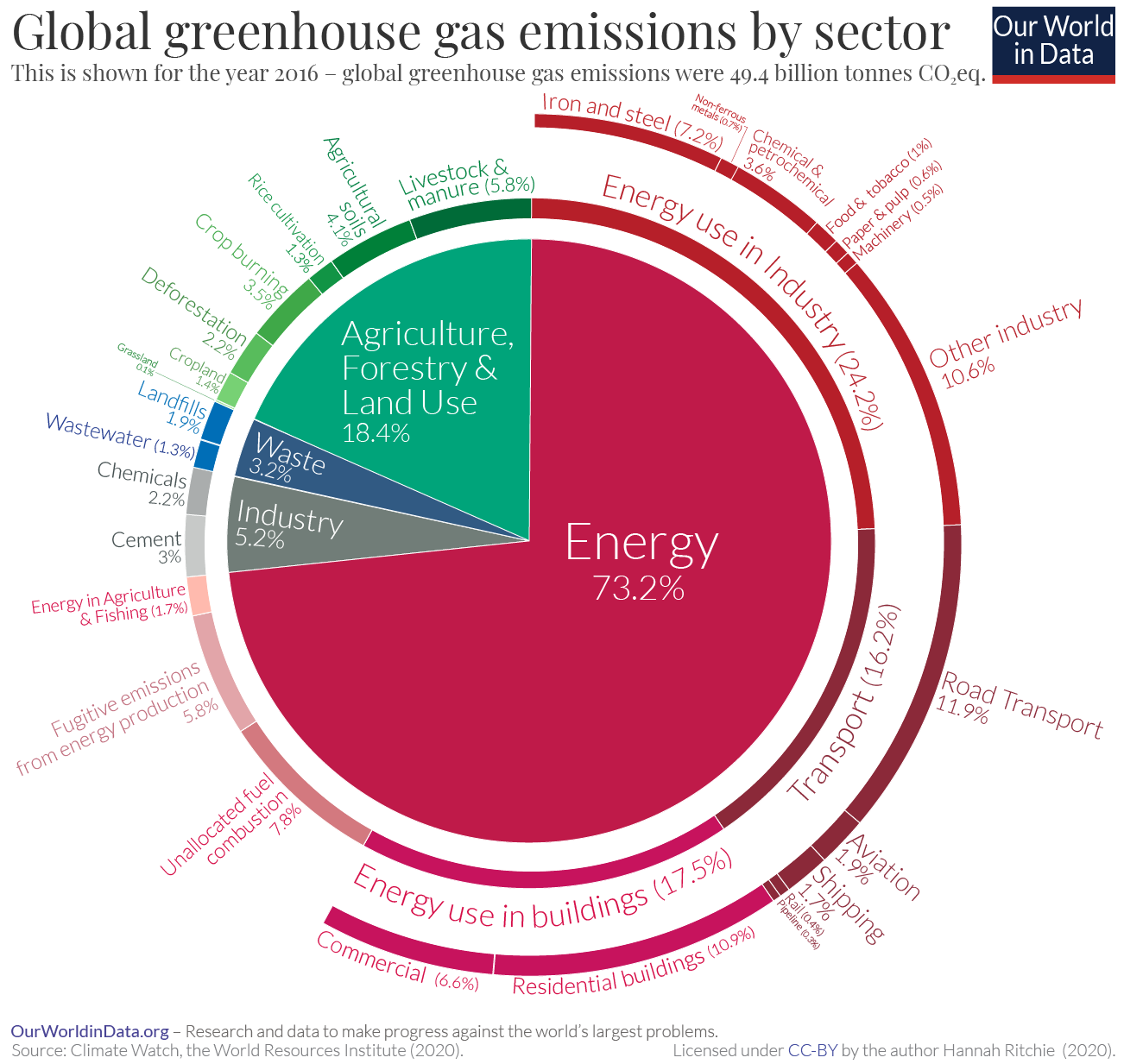



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data
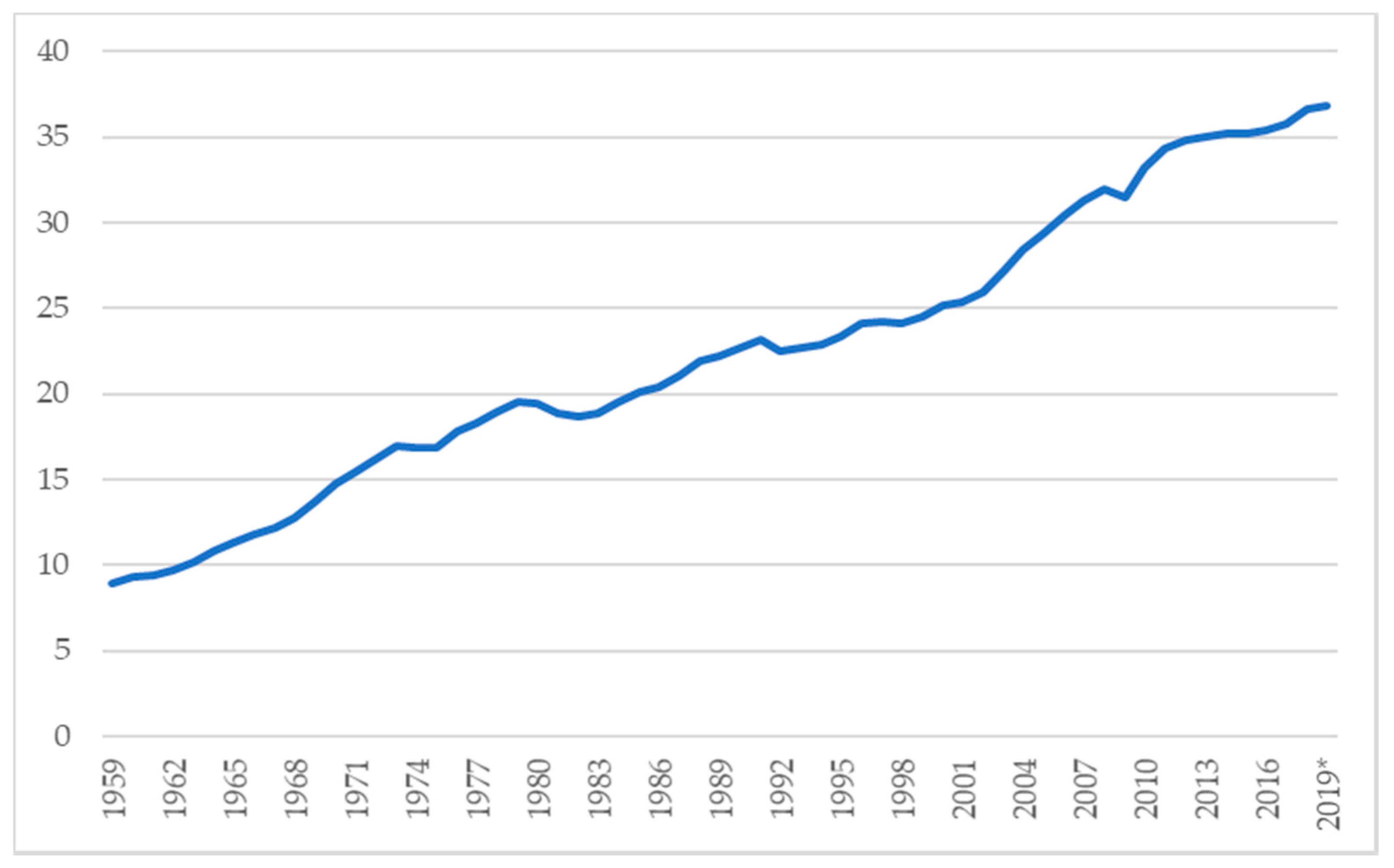
Global CO 2 emissions from coal use declined by almost 0 million tonnes (Mt), or 13%, from 18 levels, offsetting increases in emissions from oil and natural gas Advanced economies saw their emissions decline by over 370 Mt (or 32%), with the power sector responsible for 85% of the drop Milder weather in many large economies compared with 18Significant impact on greenhouse gas emissions in the UK over this period • Carbon dioxide (CO 2) emissions in the UK are provisionally estimated to have fallen by 107% in from 19, to 3261 million tonnes (Mt), and total greenhouse gas emissions by % to 4141 million tonnes carbon dioxide equivalent (MtCO 2 e) Total greenhouse gasIn this chart we see the growth of global emissions from the mid18th century through to today We see that prior to the Industrial Revolution, emissions were very low Growth in emissions was still relatively slow until the midth century In 1950 the world emitted 6 billion tonnes of CO2




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Plunged 17 Percent During Pandemic The Washington Post
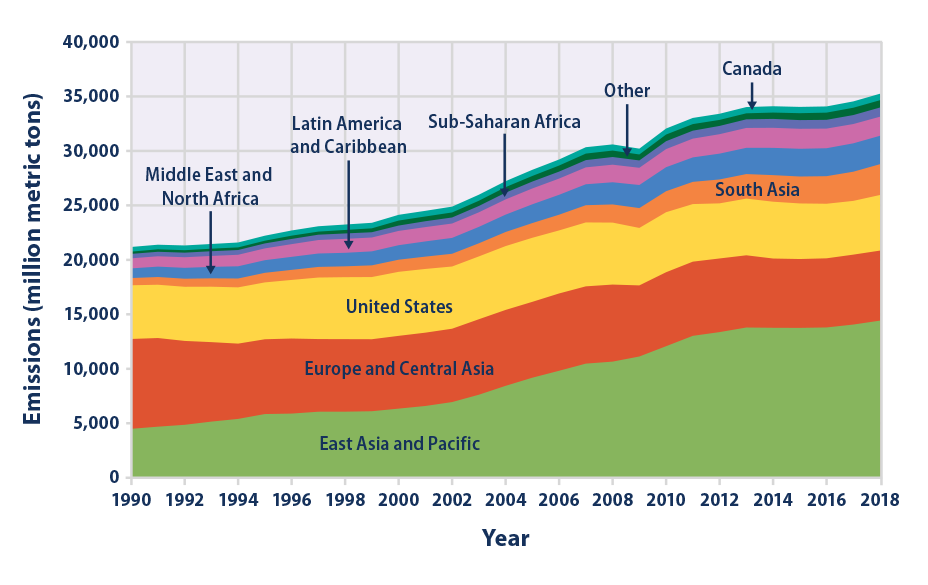



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
Human activities are responsible for almost all of the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere over the last 150 years 1 The largest source of greenhouse gas emissions from human activities in the United States is from burning fossil fuels for The benefits of reduced greenhouse gas emissions occur on the same timescale as the political decisions that lead to those reductions Without major action to reduce emissions, global temperature is on track to rise by 25 °C to 45 °C (45 °F to 8 °F) by 2100, according to the latest estimatesAt the time of report completion, 126 countries covering 51 per cent of global greenhouse gas emissions had adopted, announced or were considering netzero goals These commitments must urgently be translated into strong nearterm policies and action, and reflected in NDCs



2
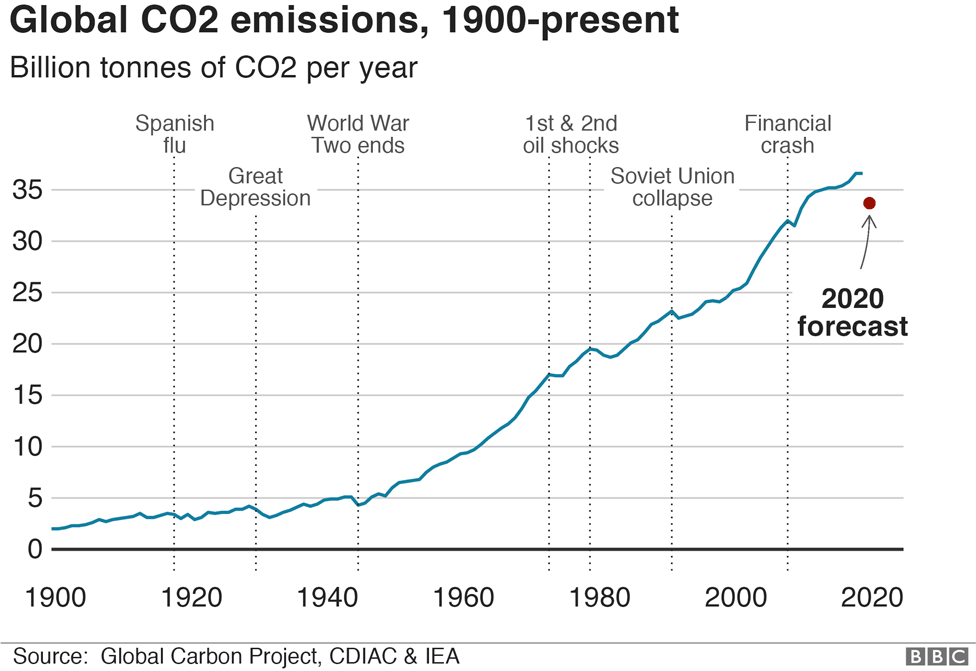



Climate Change And Coronavirus Five Charts About The Biggest Carbon Crash c News
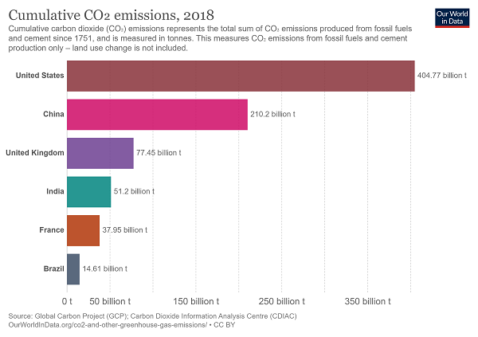
And target setting, greenhouse gases are generally measured by global warming potential (GWP), a measure of how much energy the emissions of one ton of gas will absorb during a given period, relative to the emissions of one ton of carbon dioxide1 GWP is calculated for a specific time span, most commonly 100 years But the lifetime for eachCO 2 is the primary anthropogenic greenhouse gas, accounting for 78% of the human contribution to the greenhouse effect in 10 4; Since 1751 the world has emitted over 15 trillion tonnes of CO 2 1 To reach our climate goal of limiting average temperature rise to 2°C, the world needs to urgently reduce emissions One common argument is that those countries which have added most to the CO 2 in our atmosphere – contributing most to the problem today – should take on the greatest responsibility
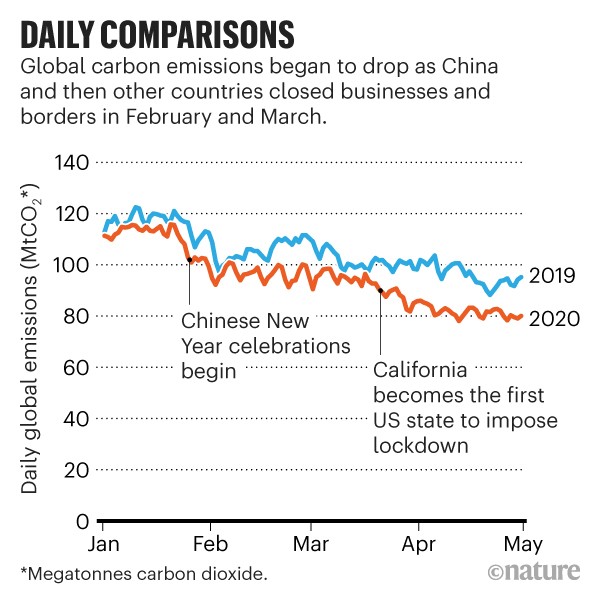



How The Coronavirus Pandemic Slashed Carbon Emissions In Five Graphs
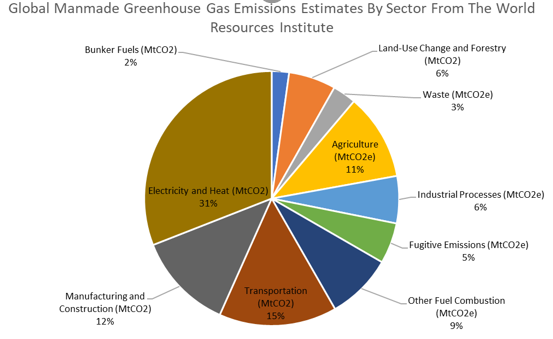



How Much Does Animal Agriculture And Eating Meat Contribute To Global Warming
According to NOAA's 19 Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (right axis), the combined heating influence of all major greenhouse gases has increased by 45% relative to 1990 Graph by NOAA Climategov based on data from NOAA ESRL According to the 19 AGGI report, the combined heating influence of the longlived, humanproduced greenhouse gases is 314 WattsPeatlands are highly significant to global efforts to combat climate change, as well as wider sustainable development goals The protection and restoration of peatlands is vital in the transition towards a lowcarbon and circular economy Damaged peatlands contribute about 10% of greenhouse gas emissions from the land use sector
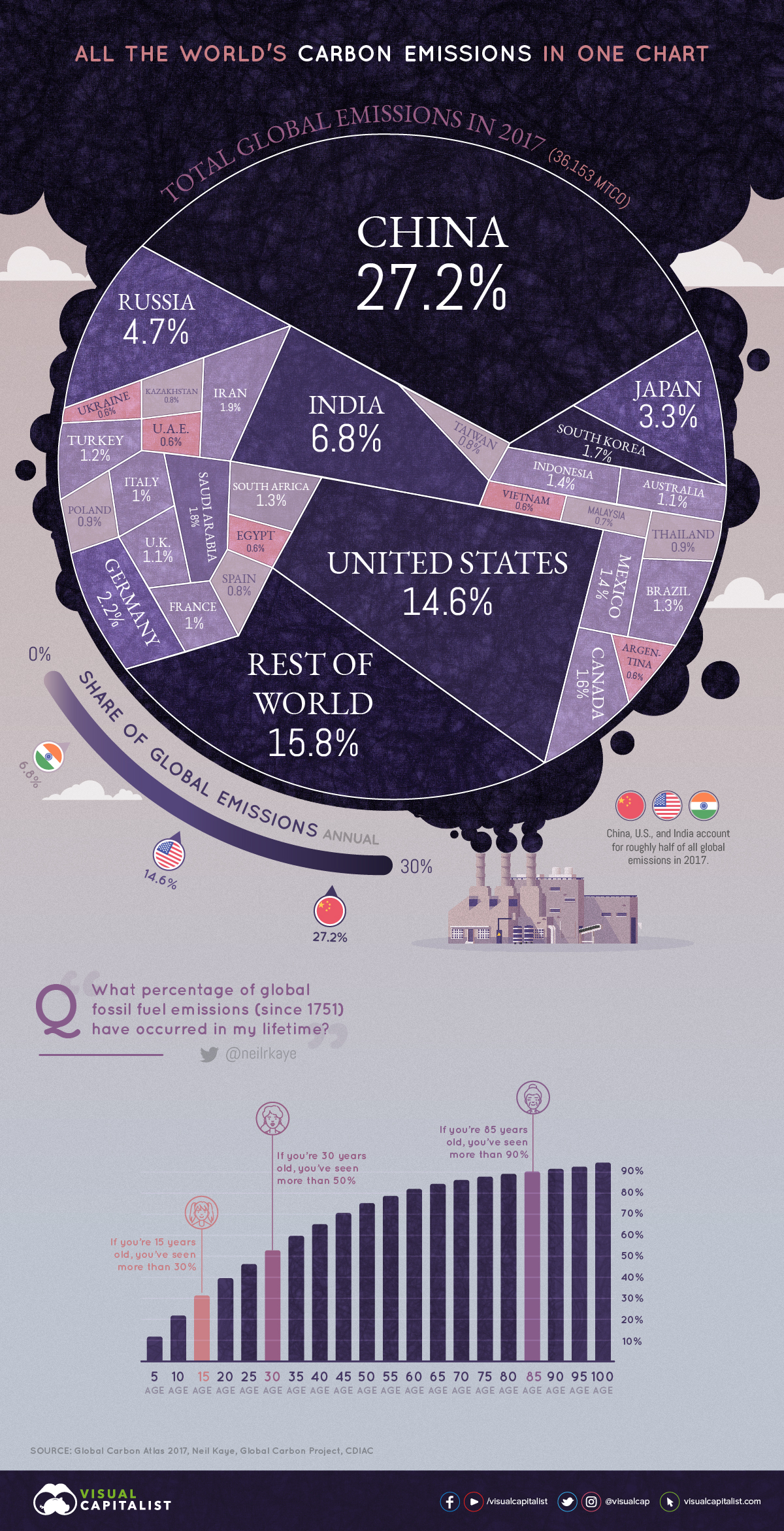



All Of The World S Carbon Emissions In One Giant Chart




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Have Already Peaked In 30 Major Cities World Economic Forum
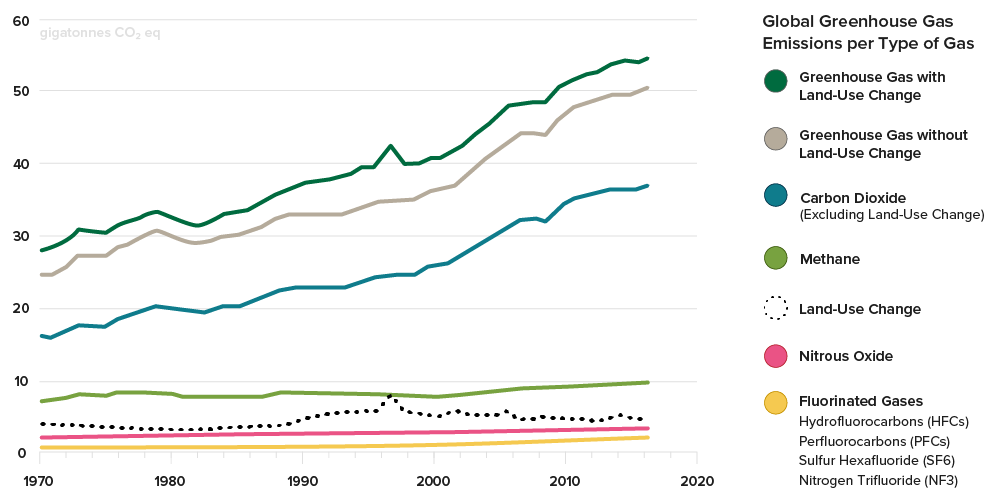



Carbon Emissions Forestry Carbon Credits The Arbor Day Foundation



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Visualizing The Most Recent Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data



B Greenhouse Gas Emission Trends Ar4 Wgiii Summary For Policymakers




Trends In Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Beaver Revolt



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data



2



National 13 And Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emission Limits Under The Effort Sharing Decision Esd Relative To 05 Emissions Levels European Environment Agency



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions In The Unmitigated Reference Download Scientific Diagram



Sustainability Free Full Text Allocation Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Using The Fairness Principle A Multi Country Analysis




More Than Half Of All Co2 Emissions Since 1751 Emitted In The Last 30 Years



2



Where Are Us Emissions After Four Years Of President Trump




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector 1990 05 In Carbon Dioxide Equivalents Epa 10 Greenhou Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



Where Are Us Emissions After Four Years Of President Trump



The Global Rise Of Emissions Trading Climate Policy Info Hub



2



File Greenhouse Gas Emissions Analysis By Source Sector Eu 28 1990 And 16 Percentage Of Total Png Statistics Explained




List Of Countries By Greenhouse Gas Emissions Per Person Wikipedia



China S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Exceeded The Developed World For The First Time In 19 Rhodium Group




Ghg Emissions Per Capita By Select Country 19 Statista
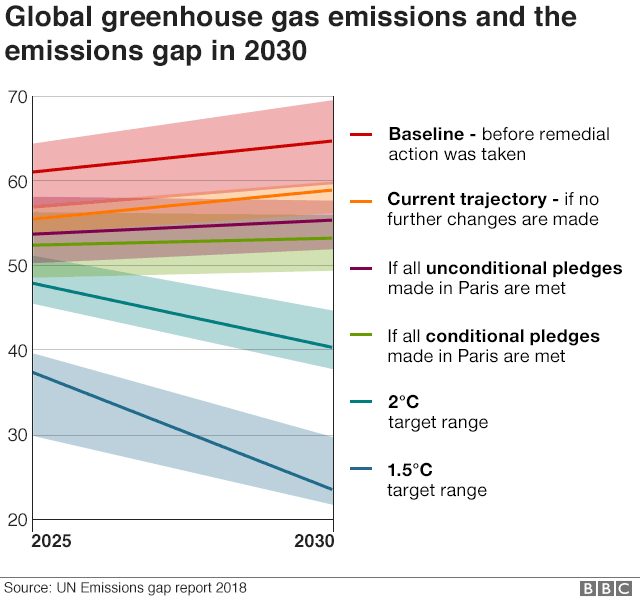



Climate Change Co2 Emissions Rising For First Time In Four Years c News



2
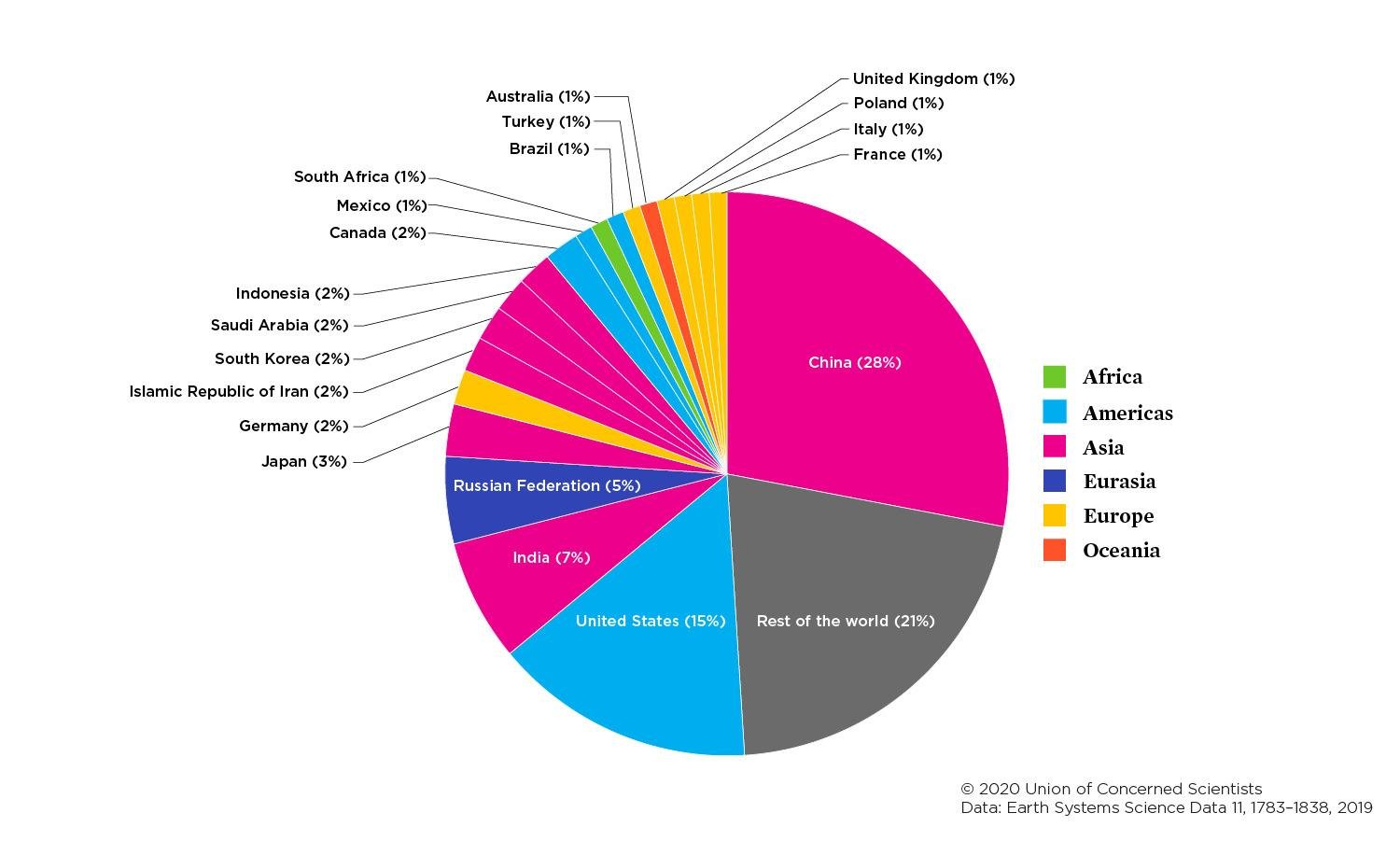



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists
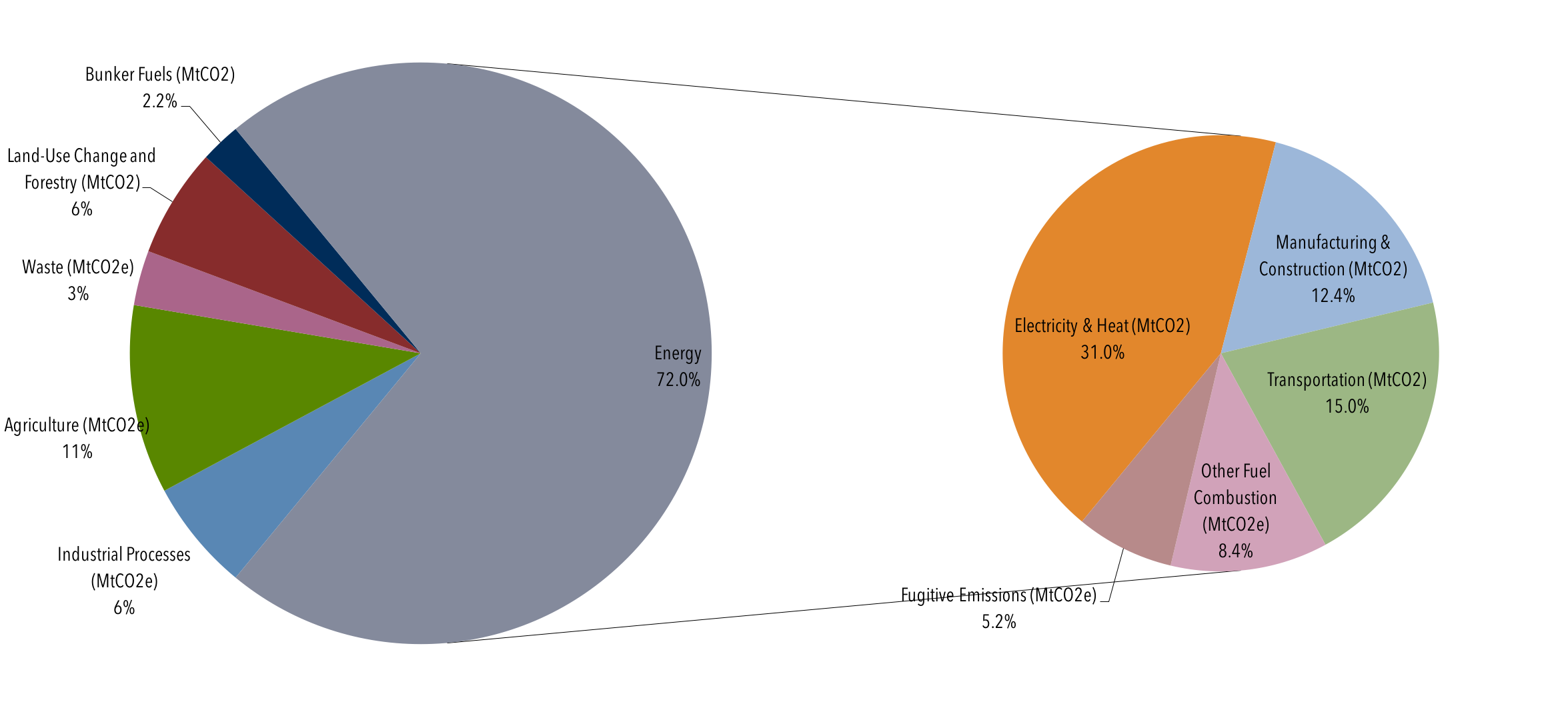



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




U S Ghg Emissions At Lowest Level In Years Climate Central




Our World In Data One Quarter Of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Food Production As We Make Progress On Low Carbon Energy Food Emissions Will Become Increasingly Important Latest Post In Our



2



Trends In Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Per Capita In Annex I And Non Annex I Countries 1970 05 European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
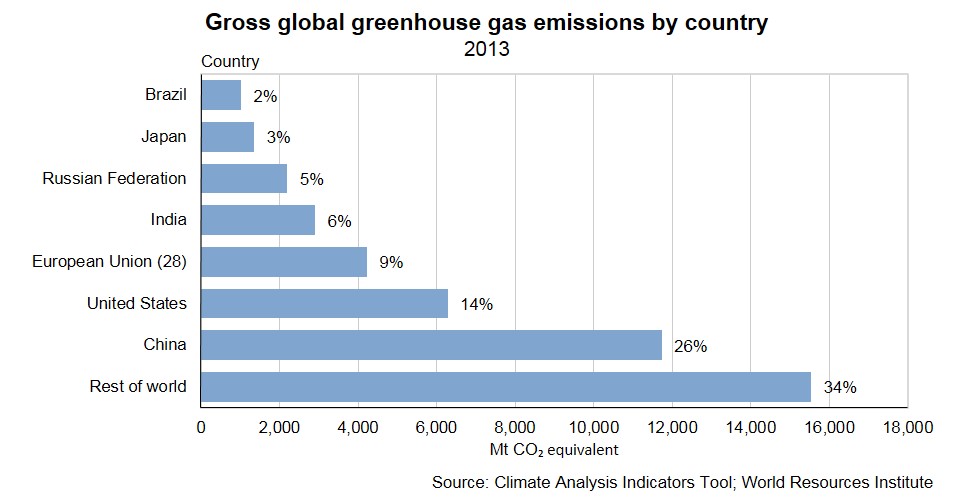



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Stats Nz




Greenhouse Gas Emission Levels Continued To Rise In 16 Pbl Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency
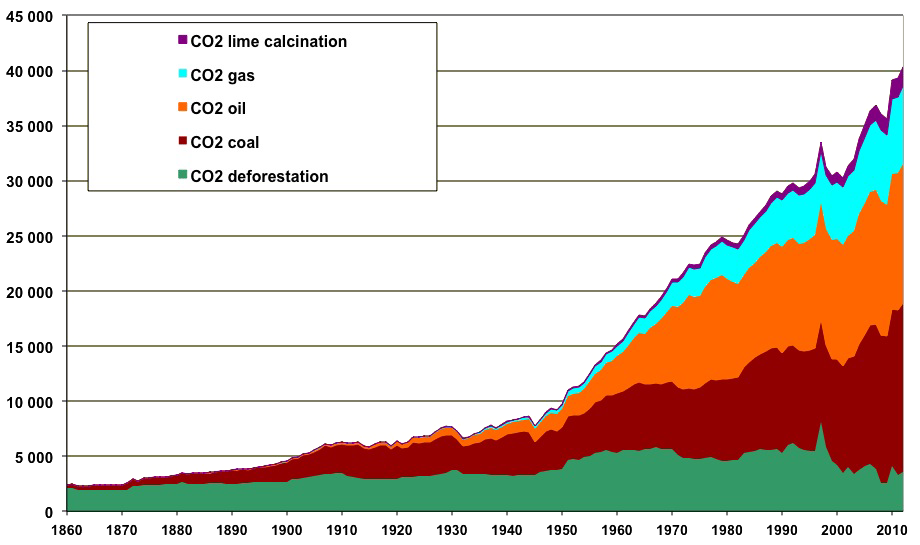



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici
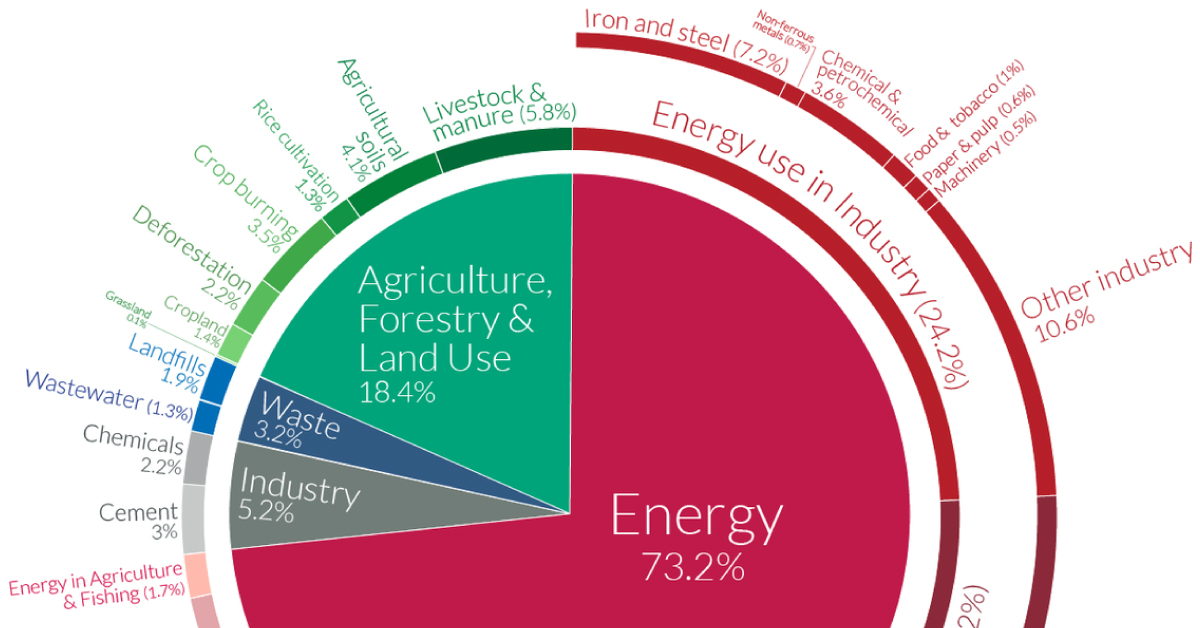



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions On The Rise Countries Falling Short On Promises Market Business News
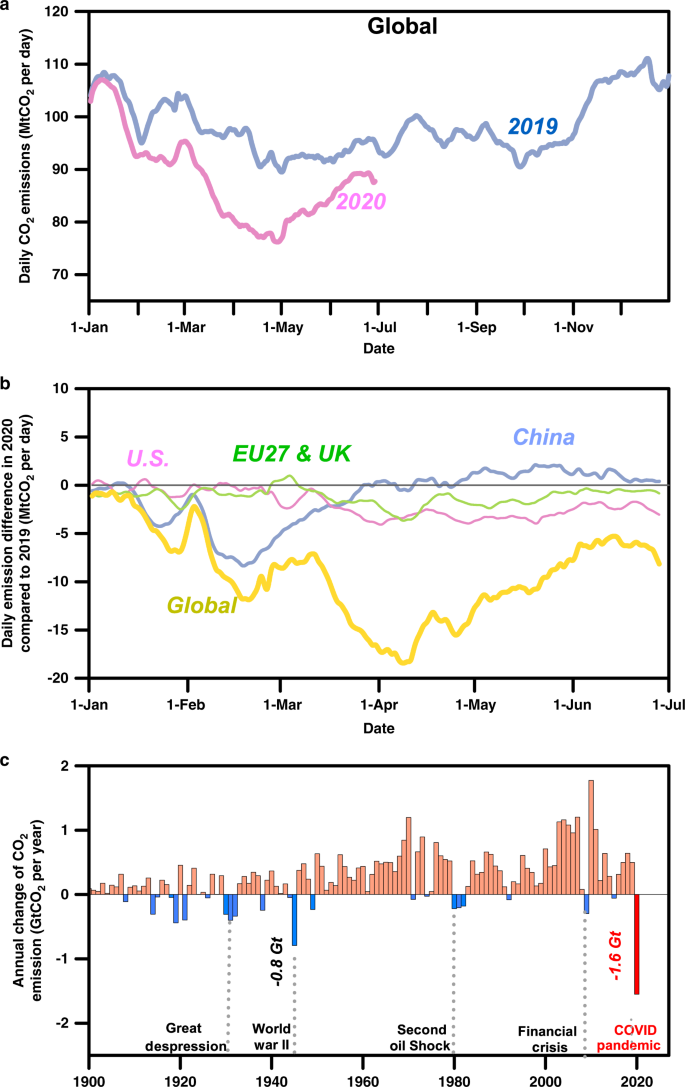



Near Real Time Monitoring Of Global Co2 Emissions Reveals The Effects Of The Covid 19 Pandemic Nature Communications




World Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector Grid Arendal
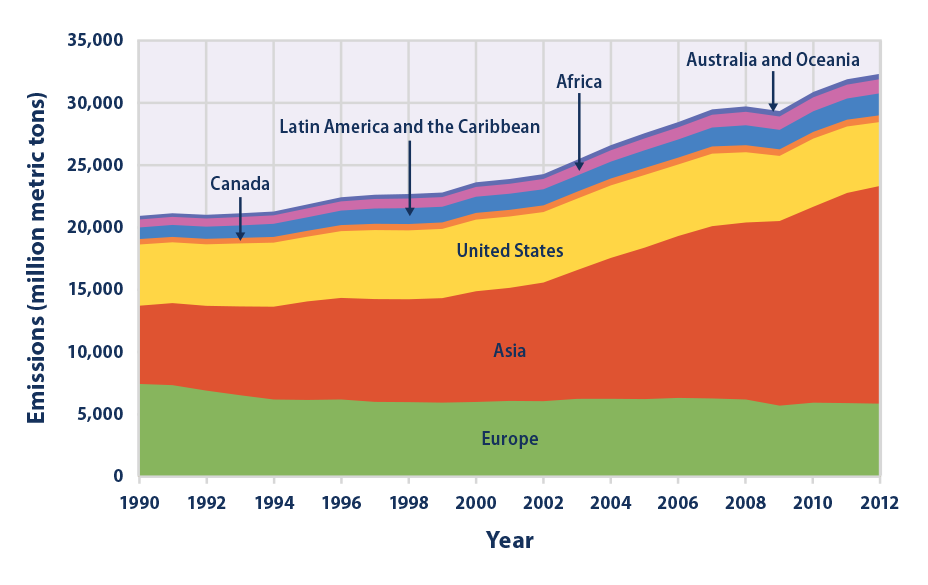



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa



3



2
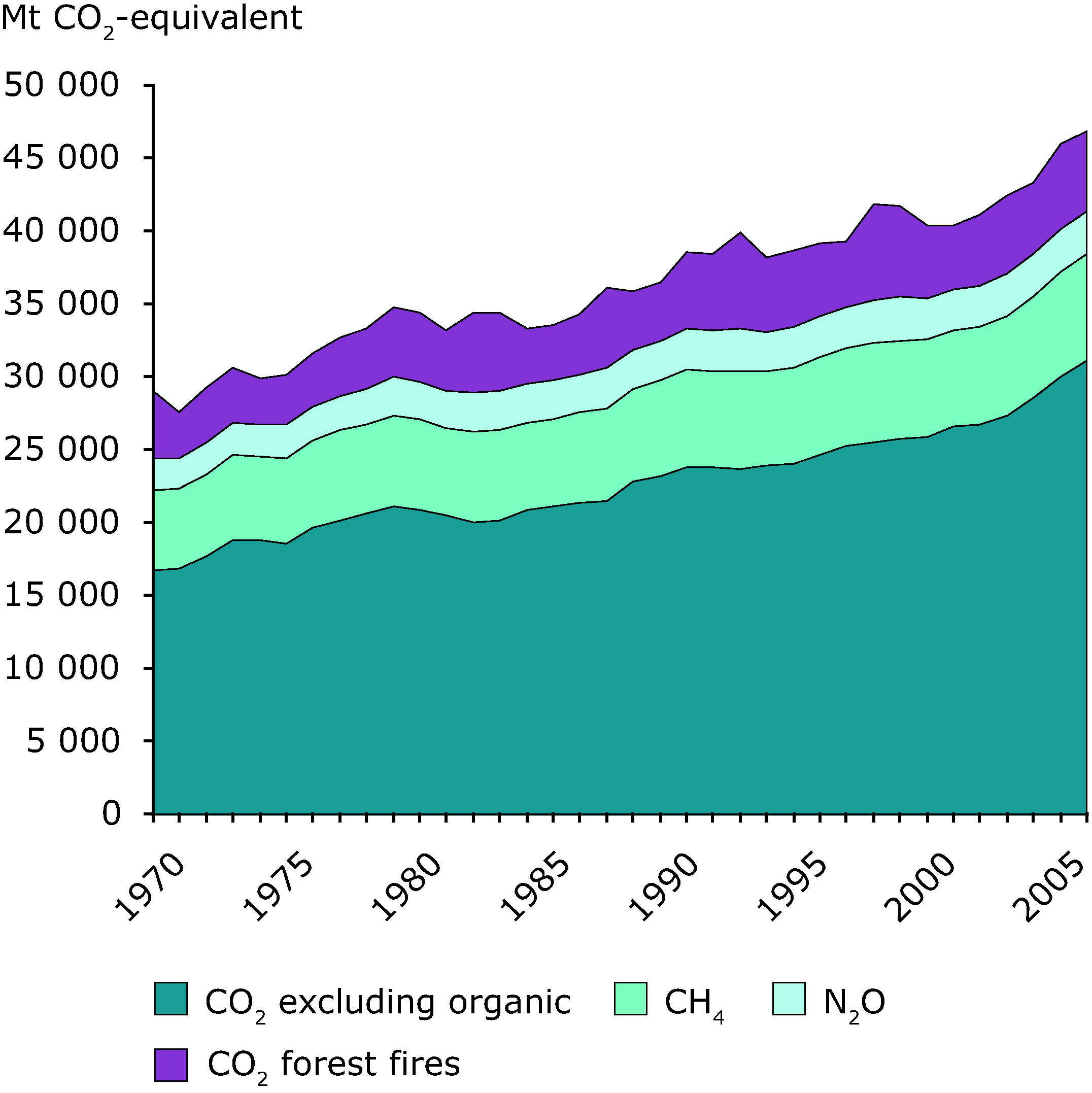



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Gas Type 1970 05 European Environment Agency



1




Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
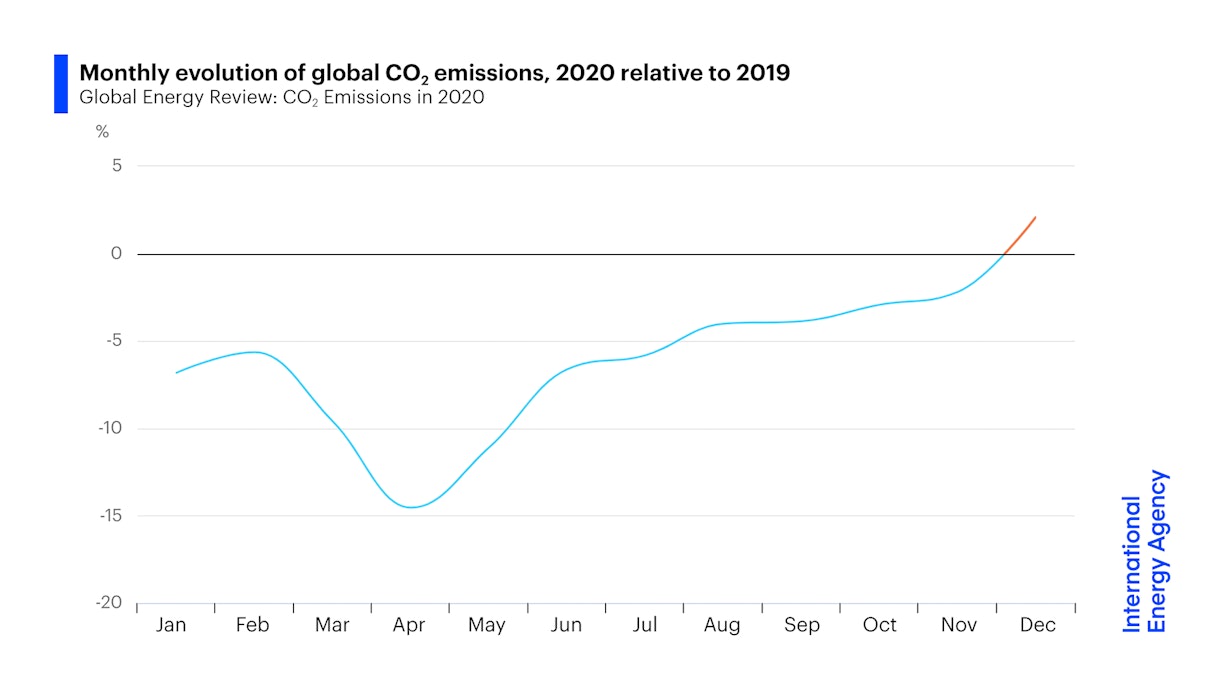



After Steep Drop In Early Global Carbon Dioxide Emissions Have Rebounded Strongly News Iea
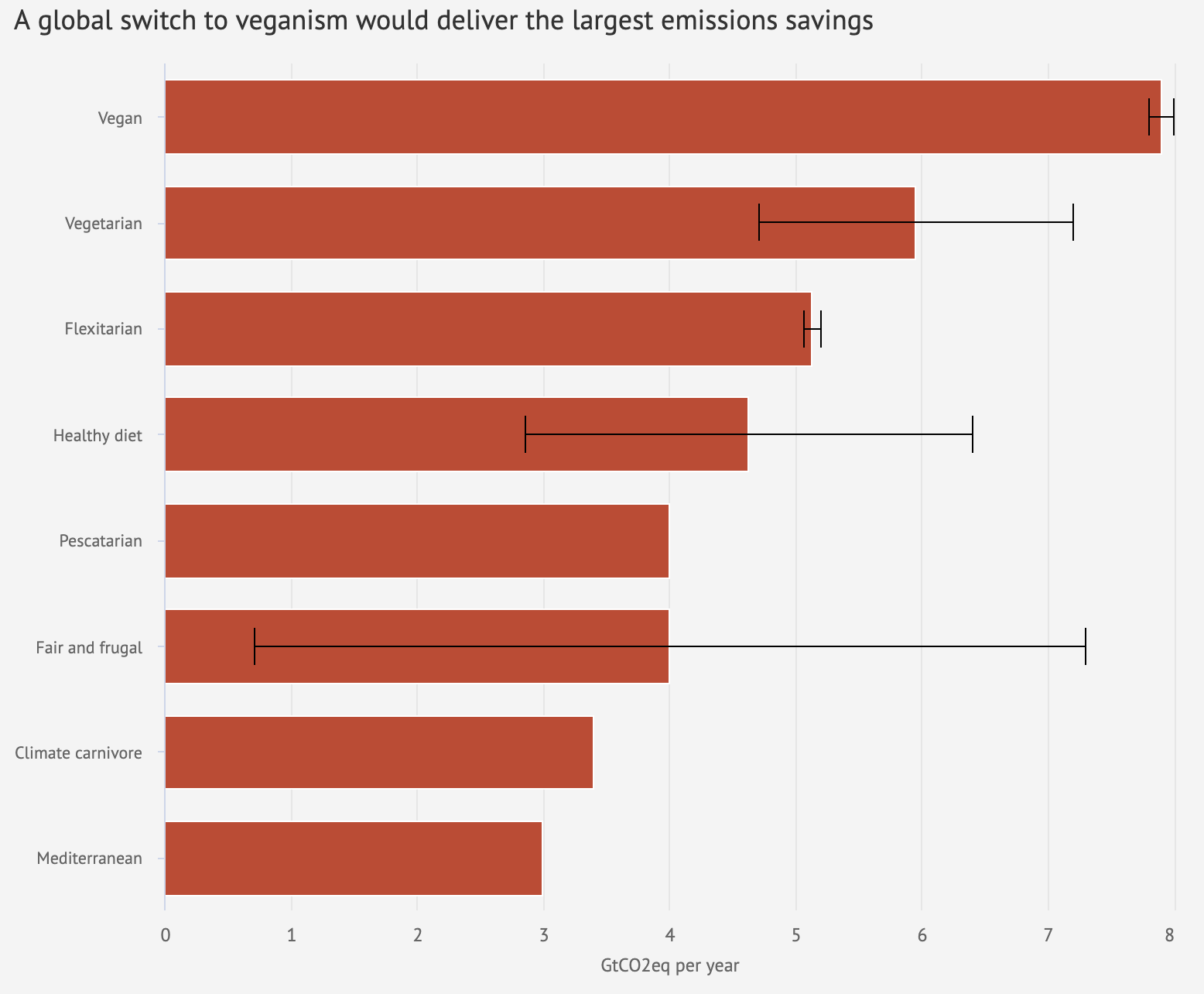



Interactive What Is The Climate Impact Of Eating Meat And Dairy Carbon Brief
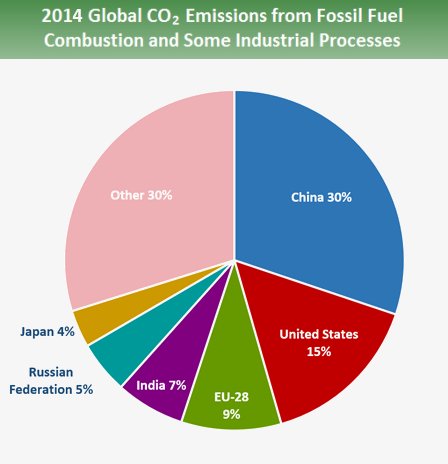



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
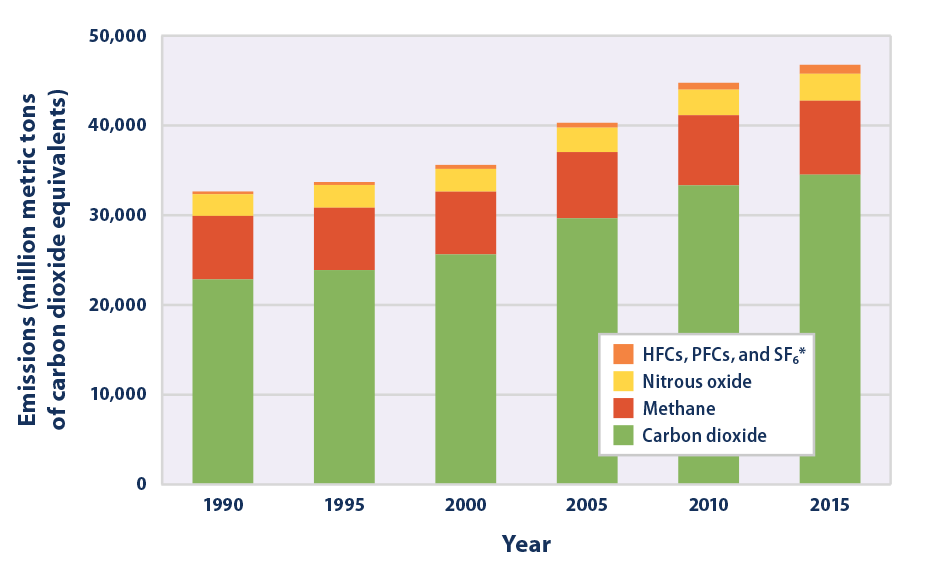



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
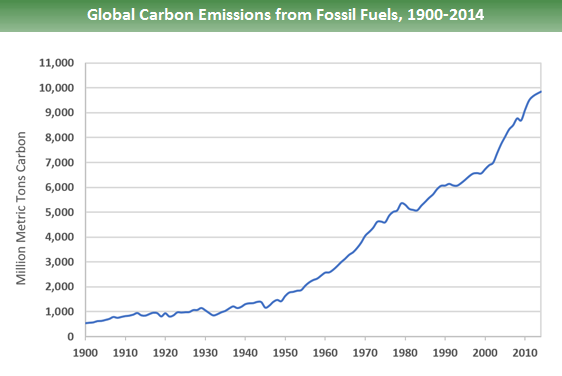



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa



1




1 Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions From All Sources Download Scientific Diagram
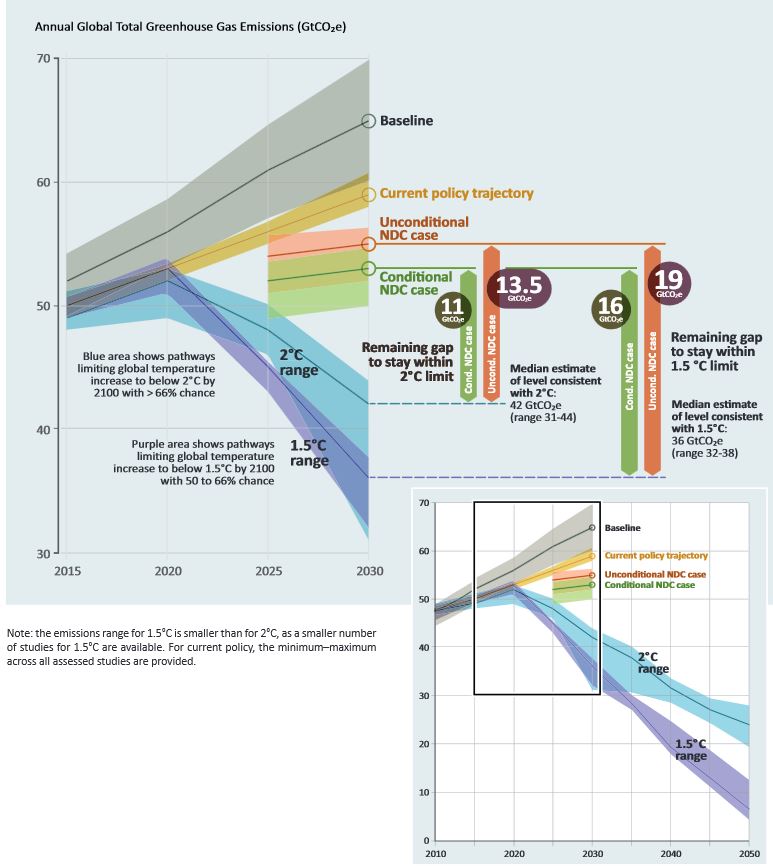



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Knowledge For Policy
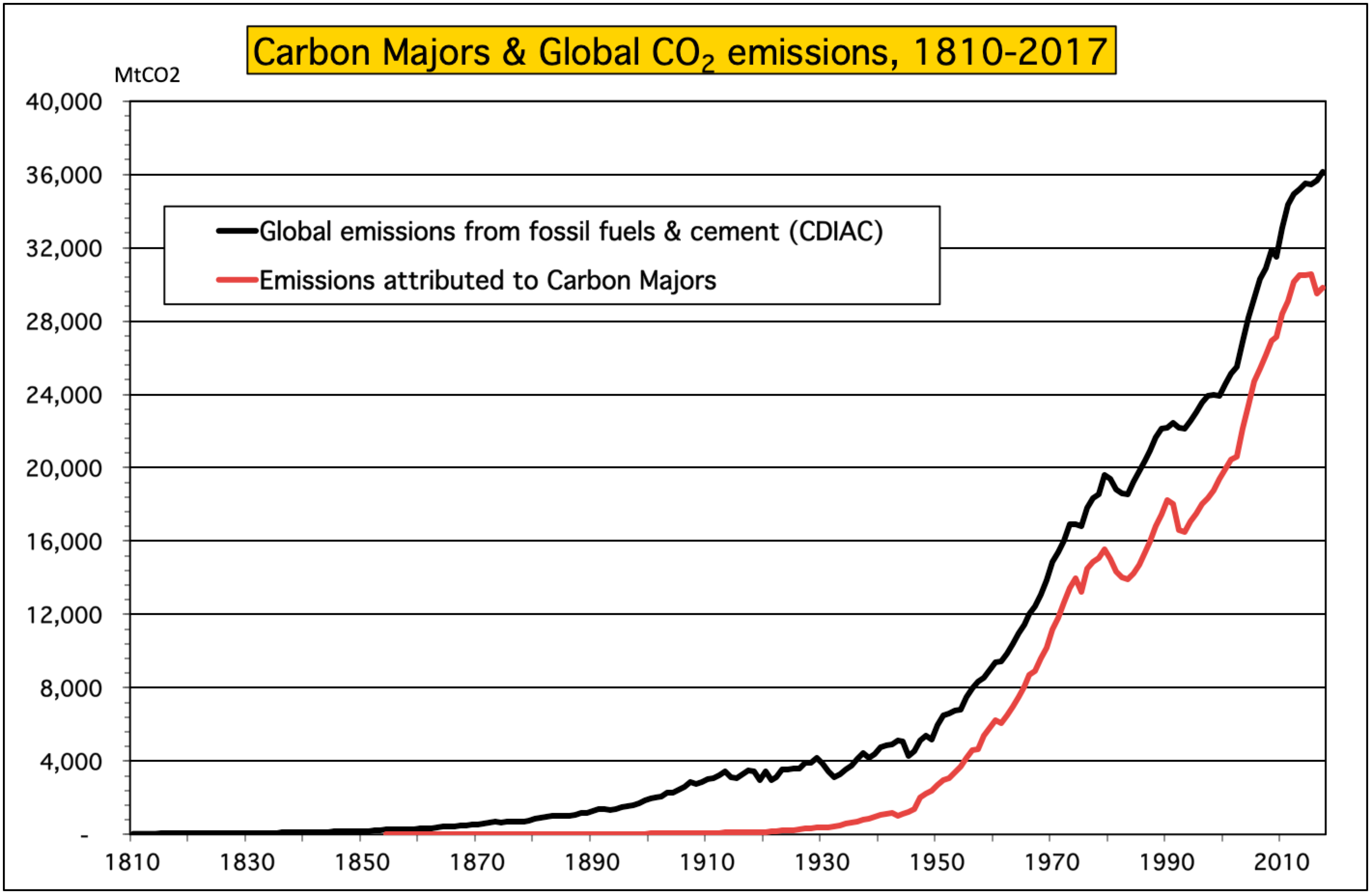



Climate Accountability Institute




Scale Distribution And Variations Of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Driven By U S Households Sciencedirect




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



2
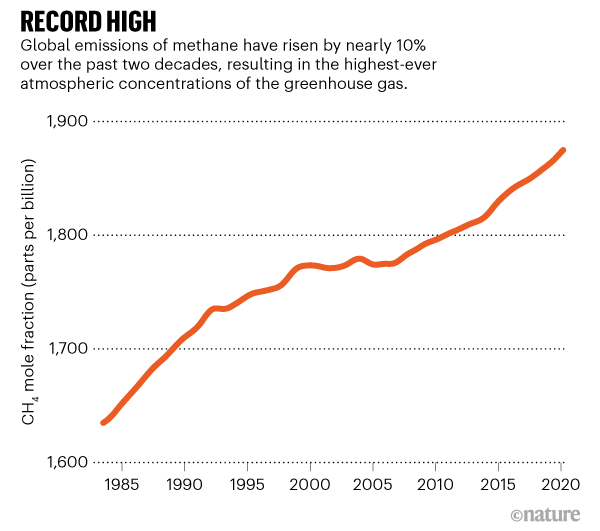



Global Methane Levels Soar To Record High



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Used Cait As Data Source Climatechange




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector Download Scientific Diagram
.png)



Fact Sheet The Growth In Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Commercial Aviation 19 White Papers Eesi




File Global Human Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector 16 Png Wikipedia
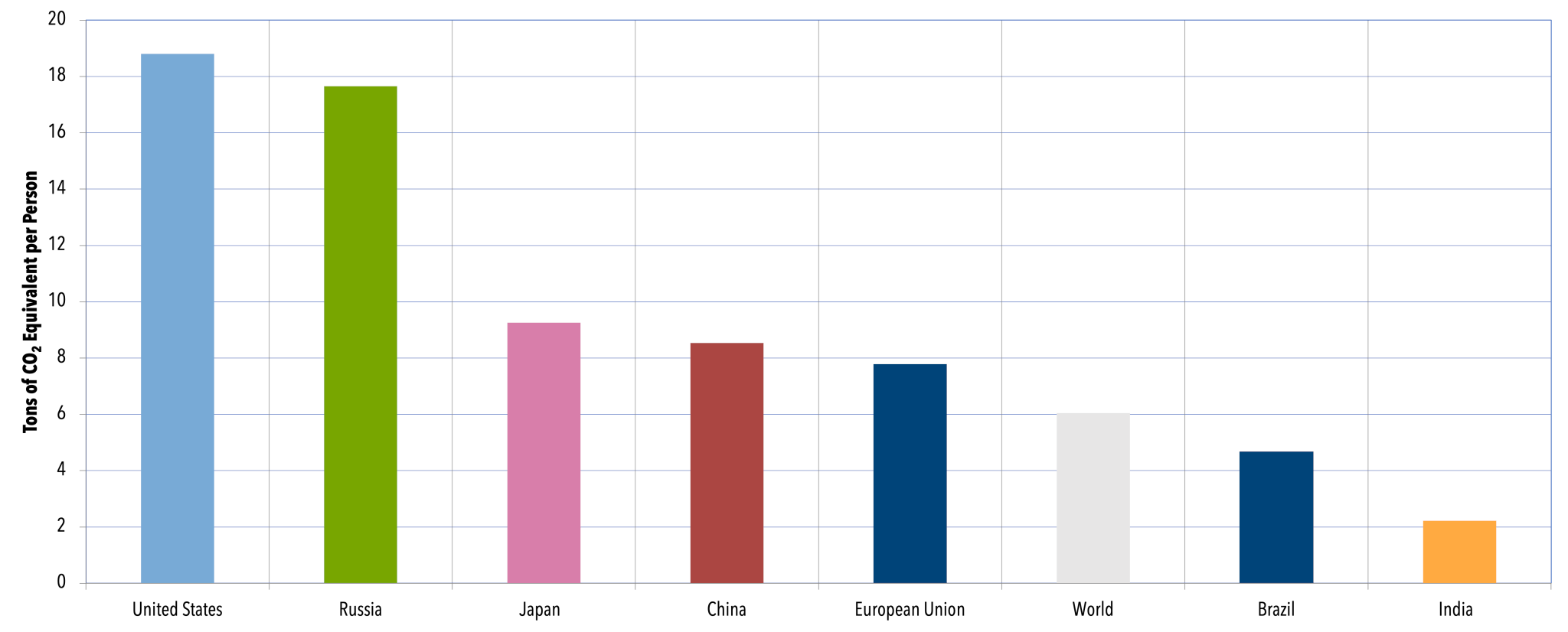



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
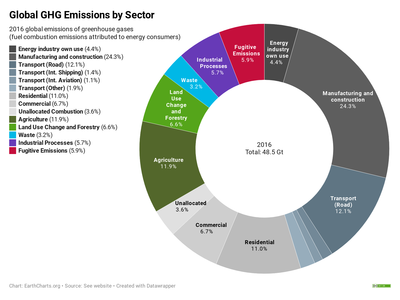



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
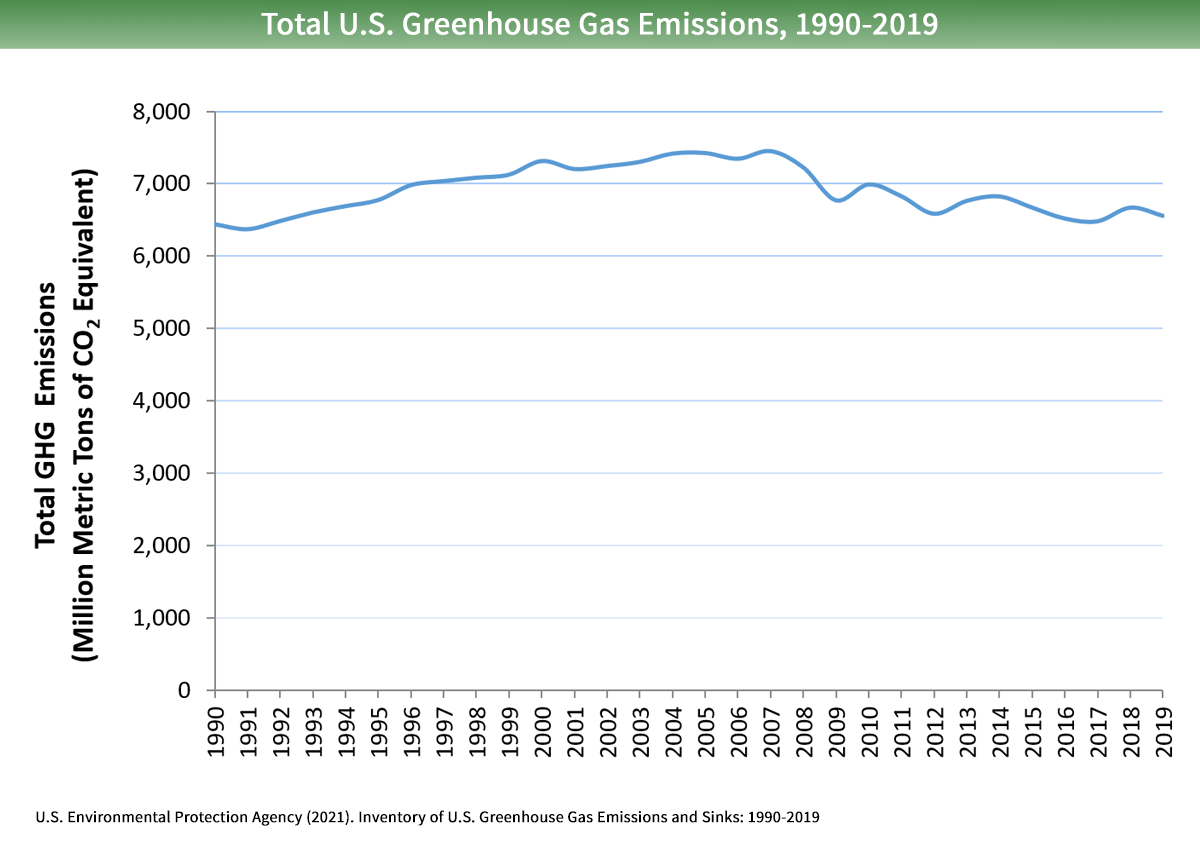



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
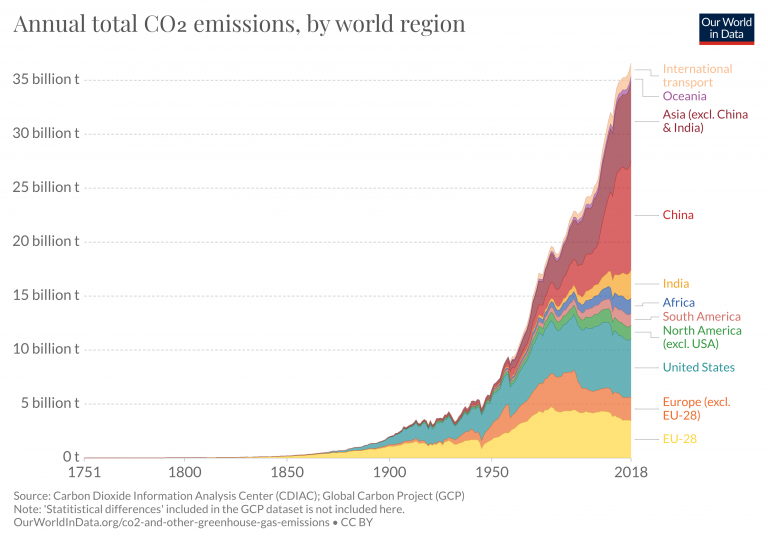



Co2 Emissions Our World In Data



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Global Greenhouse Emissions A Good News Bad News Story Nrdc
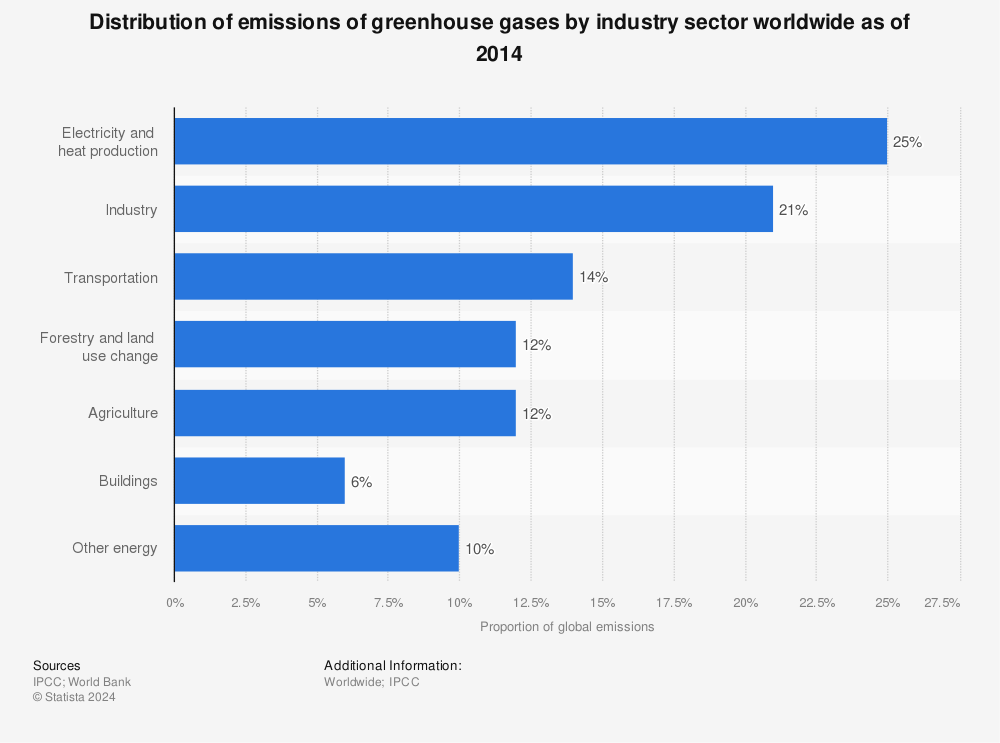



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector 14 Statista
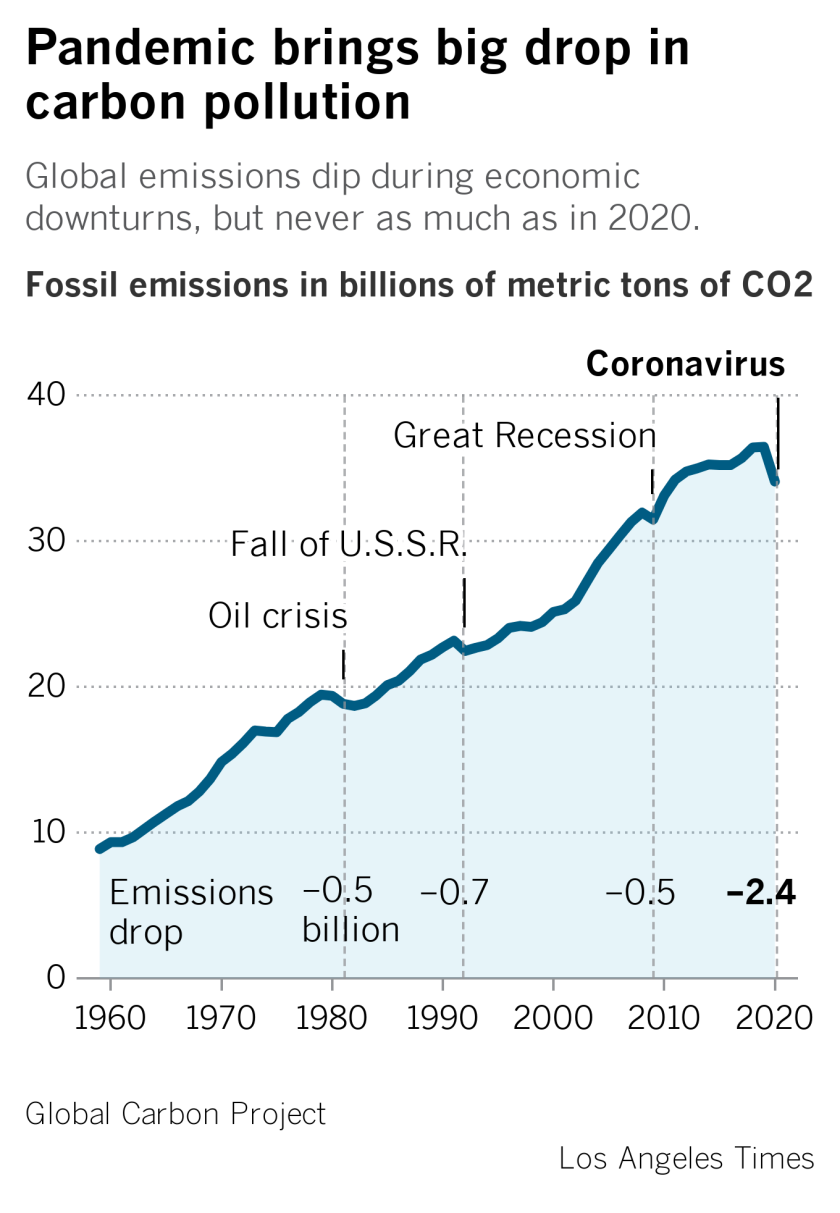



Global Carbon Emissions Dropped 7 Amid Covid 19 Los Angeles Times
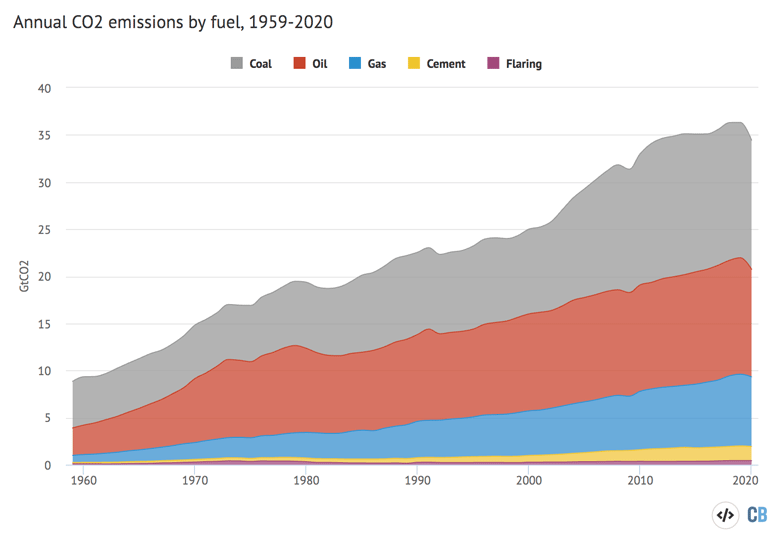



Global Carbon Project Coronavirus Causes Record Fall In Fossil Fuel Emissions In Carbon Brief
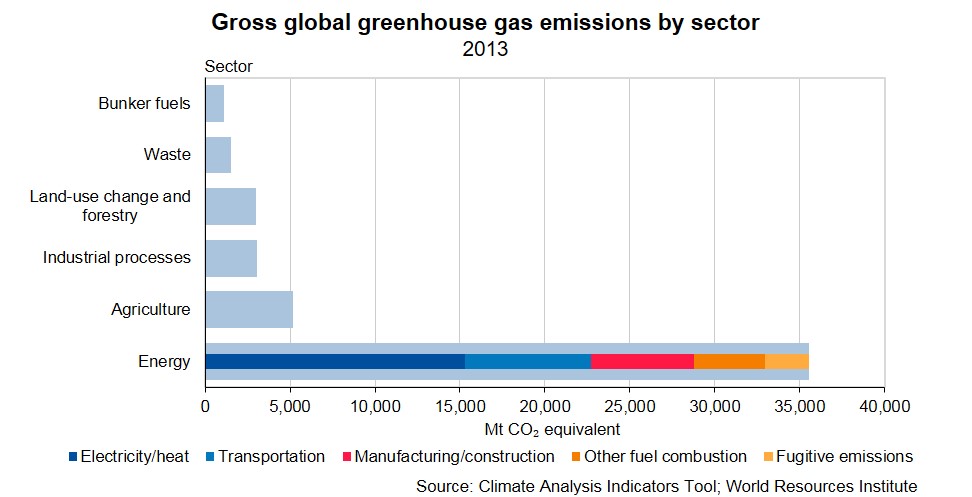



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Stats Nz
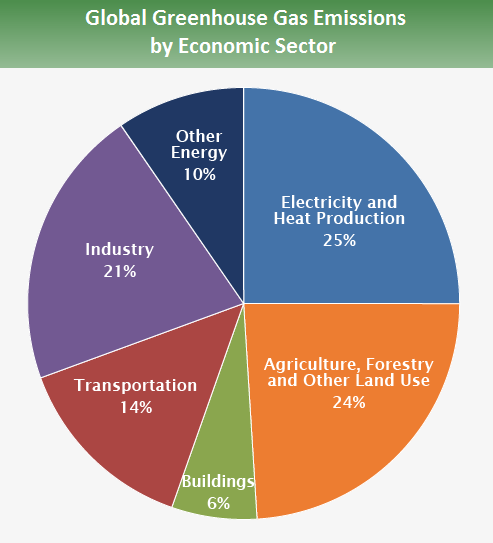



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
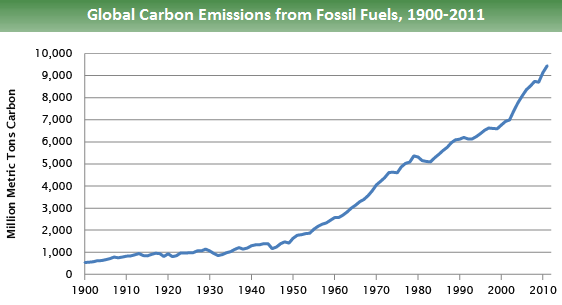



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
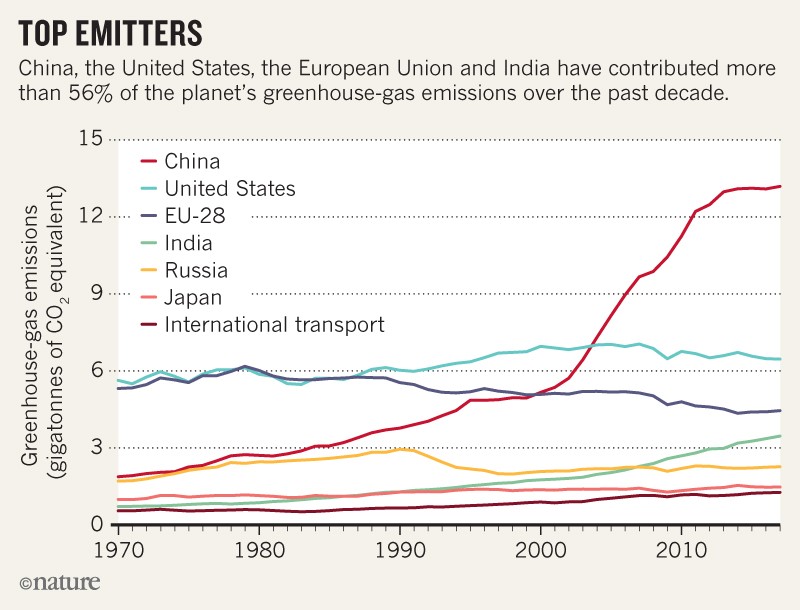



Nations Must Triple Efforts To Curb Greenhouse Gas Emissions



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




How Each Country S Share Of Global Co2 Emissions Changes Over Time World Economic Forum




France Greenhouse Gas Emissions Decreased By 16 9 From 1990 Levels Climate Scorecard




Transportation Ghg Emissions Worldwide 1990 18 Statista




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Livestock Knoema Com



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data
コメント
コメントを投稿